Navigating the rising cost of student living
- Fiona Vaz

- Aug 15, 2024
- 2 min read
Updated: Oct 25, 2024
Fiona Vaz
Today, students from across the country are relocating to major cities to access better educational opportunities. As they make this move, they must develop strong financial management skills to cope with the rising costs and inflation. Students incur expenses for accommodation, food, transportation, groceries, outings, educational materials, health care, and unexpected emergencies, all within a limited allowance. As a result, many students find themselves with little to no savings after covering these essential costs.
Watch this video to know how much youngsters spend in Bengaluru.
So how does a student save money?
The year-on-year rise in inflation stands as a hindrance to students looking for quality education. A few methods students can use to tackle these expenses are budgeting, and making a financial plan.
Source: Prodigy Finance
Budgeting
According to Investopedia, Budgeting refers to estimating revenue and expenses made for a certain period. Making a budget for expenses is beneficial to a student as it provides clarity on the expenses made. Keeping track of major and minor expenses will result in knowing how much to save, furthermore preparing for unexpected expenses.
The United National Federal Credit Union (UNFCU) suggests the ‘50-30-20’ rule to organise expenditures into needs, wants, and goals. This budget rule aims to provide an individual with a smart method of financing.
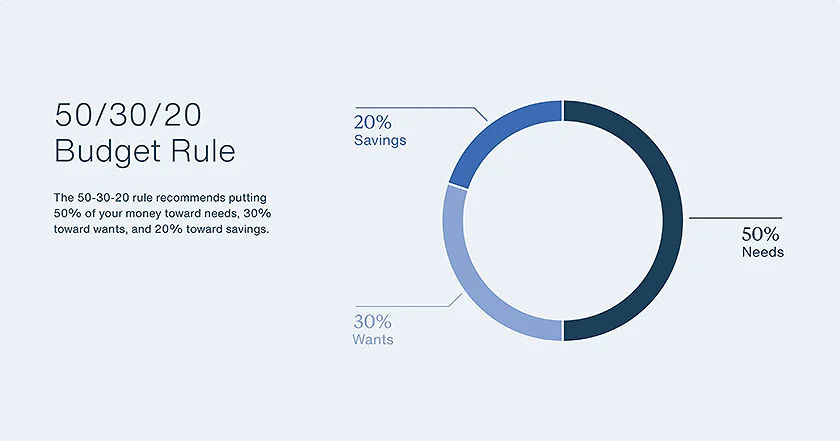
Source: UNCFU
It explains that ‘Needs’ include utility bills, rent, healthcare, and groceries, ‘Wants’ consist of subscriptions, experiences, restaurant meals and vacations, and ‘Savings’ include money for future goals.
Financial Goals
True Tramplin in his article Financial Goals, defines these goals as specific objectives individuals set to achieve financial success. Financial Goals provide a sense of direction and drive towards achieving a desired outcome. Depending on the student’s financial circumstances and aspirations, setting five long-term goals can build healthy money habits.
For example:
1. Building an emergency fund for unexpected crises.
2. Paying off student loans early to avoid higher interest rates and open cash flow.
3. Saving for major life events (higher education, marriage, vehicles, housing, starting a family or other needs)
4. Learning how to invest early on in your career.
5. Maintaining a good credit score to have a secure line of credit for the future.
Spending wisely will not only save but also sustain more money to pursue a student’s long-term wants and desires.
Students can also check out these fun methods to budget:







Comments